Demonstrates how to perform recognition of machining features on a 3D model and print information about found features and their parameters in a console.
This example demonstrates how to perform recognition of machining features on a 3D model using machining feature recognition tool (Machining_FeatureRecognizer). For this purpose, used a console application that imports a model, traverses through unique ModelData_Part , creates and runs Machining_FeatureRecognizer, groups and prints information about found features and their parameters into console. Machining feature recognition will be performed for each unique ModelData_Part , but only for the scope of accepted geometries.
Application needs 2 input arguments to run:
For more information about feature recognition visit CNC Machining page.
PartProcessor class is inherited from SolidProcessor and overrides ProcessSolid method that are used to run Machining_FeatureRecognizer on given shape. The Machining_FeatureRecognizerParameters.SetOperation() method of the tool parameters is used to set the type of operation (Milling or LatheMilling). The operation type will be taking into account during recognition process and the recognition result will be different depending on it. Then PrintFeatures method is used to print information about found features and their parameters in a console.
Visit Model Explore Helper Implementation page for more information about base SolidProcessor class implementation.
To traverse only unique parts of the imported model, the ModelData_ModelElementUniqueVisitor class is used.
After performing feature recognition, the object of FeatureGroupManager class is used to group and sort found machining features. For this purpose, there is a traverse through all found features and add each of them to FeatureGroupManager with a specified name.
After adding all found features to FeatureGroupManager, a Print method of the manager is used to print information about found features and their parameters in a console. PrintFeatureParameters is created to explore and print feature parameters. It uses as an input parameter of Print method.
Visit Feature Group Helper Implementation page for more information about FeatureGroupManager class implementation.
The first is an example output for model from ./examples/models/Fresamento_CAM1_v3.stp and operation set to Milling. and the second one is an output for model from ./examples/models/senthi.step and operation set to Lathe+Milling.
| Model | Example output |
|---|---|
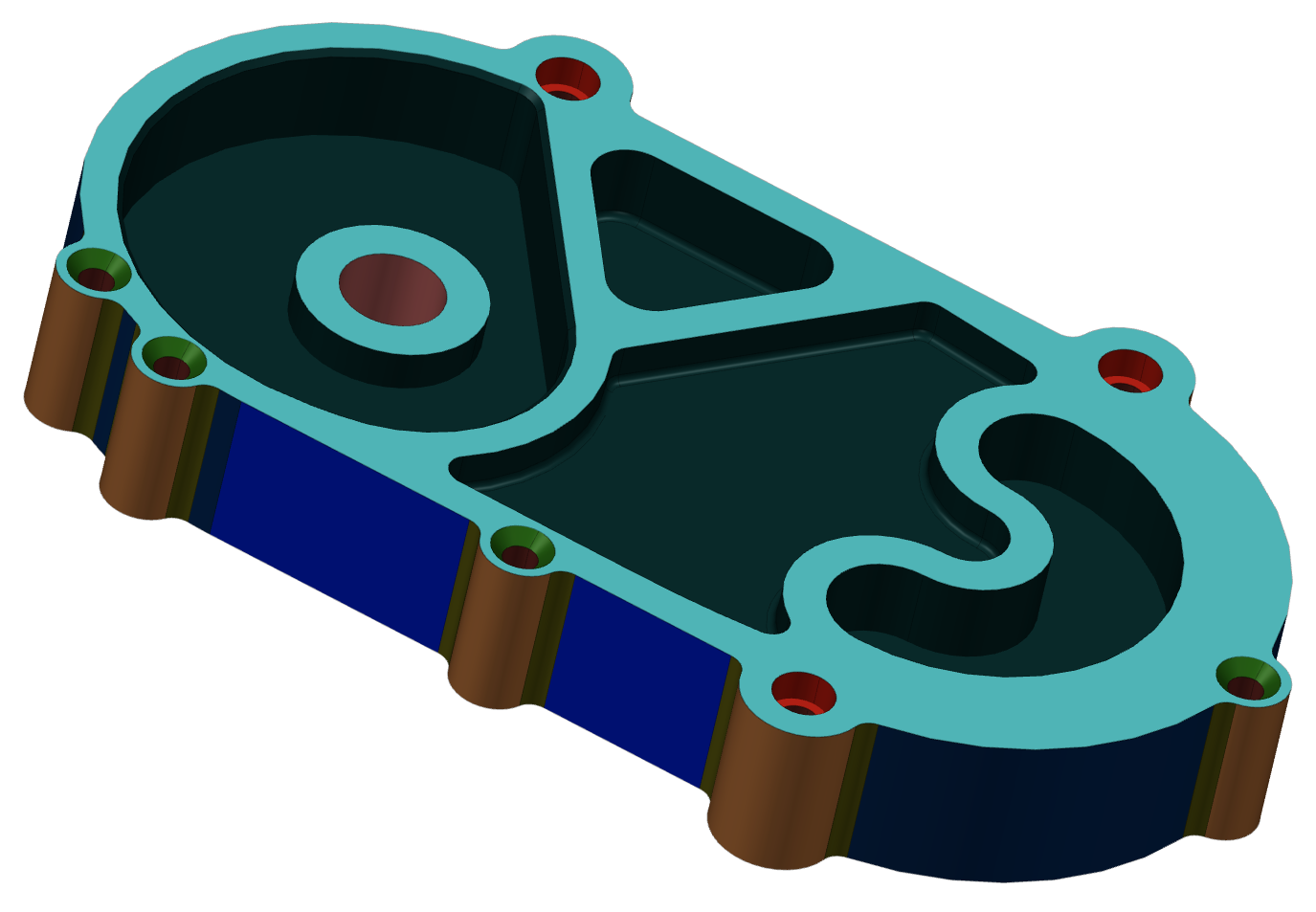
| Model: Fresamento_CAM1_v3
Part #0 ["Fresamento_CAM1"] - solid #0 has:
Concave Fillet Edge Milling Face(s): 14
14 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 5 mm
Convex Profile Edge Milling Face(s): 7
4 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 10 mm
3 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 15 mm
...
Total features: 44
|
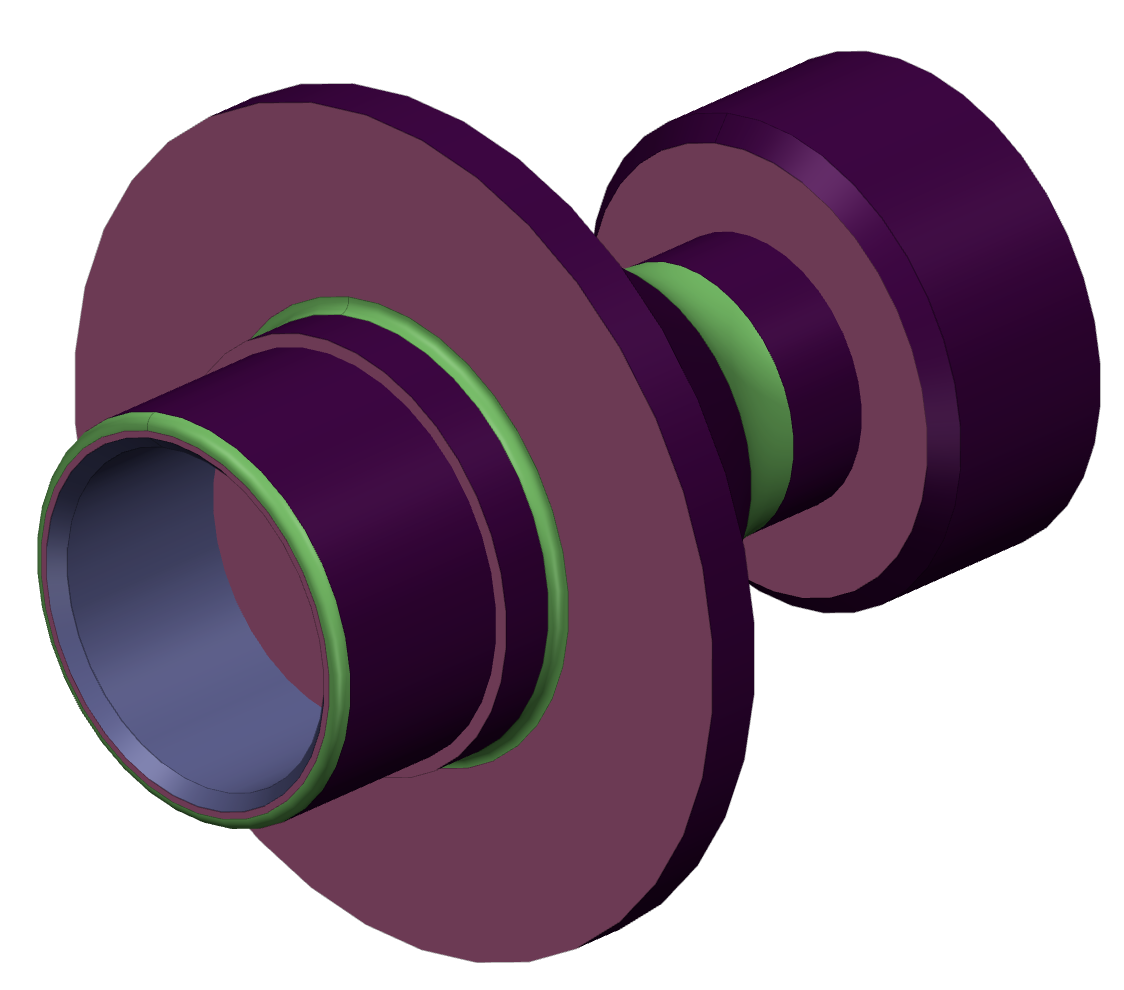
| Model: senthi
Part #0 ["drawing no 1"] - solid #0 has:
Turn Diameter Face(s): 7
1 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 50 mm
1 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 75 mm
1 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 80 mm
1 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 86 mm
1 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 90 mm
1 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 96.4288 mm
1 Turning Face(s) with
radius: 155 mm
...
Total features: 17
|