Defines a surface of revolution. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| SurfaceOfRevolution (global::System.IntPtr cPtr, bool cMemoryOwn) | |
| SurfaceOfRevolution (cadex.Geom.Curve theBasisCurve, cadex.Geom.Point theLocation, cadex.Geom.Direction theDirection) | |
| Constructor. | |
| cadex.Geom.Point | Location () |
| Returns the value specified in the constructor. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.SweptSurface Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.SweptSurface | |
| SweptSurface (global::System.IntPtr cPtr, bool cMemoryOwn) | |
| cadex.Geom.Curve | BasisCurve () |
| cadex.Geom.Direction | Direction () |
 Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.Surface Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.Surface | |
| Surface (global::System.IntPtr cPtr, bool cMemoryOwn) | |
| cadex.Geom.SurfaceType | Type () |
| Returns a surface type. | |
| cadex.Geom.Continuity | Continuity () |
| Returns a continuity type of the surface. | |
| cadex.Geom.Point | Value (double theParameterU, double theParameterV) |
| theParameterU must be within [UMin(), UMax()] if the surface is not U-periodic. | |
| cadex.Geom.Direction | Normal (double theParameterU, double theParameterV) |
| bool | IsUPeriodic () |
| Examples include sphere, torus or a surface of revolution. | |
| bool | IsVPeriodic () |
| Examples include torus or a V-periodic B-Spline. | |
| double | UMin () |
| Returns a minimum parameter of a definition domain in U direction. | |
| double | UMax () |
| Returns a maximum parameter of a definition domain in U direction. | |
| double | VMin () |
| Returns a minimum parameter of a definition domain in V direction. | |
| double | VMax () |
| Returns a maximum parameter of a definition domain in V direction. | |
| void | Domain (out double theUMin, out double theUMax, out double theVMin, out double theVMax) |
| Returns a definition domain. | |
| bool | IsTrimmed () |
| Returns whether surface is trimmed or not. | |
| void | SetTrim (double theUFirst, double theULast, double theVFirst, double theVLast) |
| Trims surface with [theUFirst, theULast] x [theVFirst, theVLast] section. | |
| void | Transform (cadex.Geom.Transformation theTransformation) |
| Results depends on the actual surface type. | |
| cadex.Geom.Surface | Transformed (cadex.Geom.Transformation theTransformation) |
| The contents of this object is not modified. | |
| void | D0 (double theParameterU, double theParameterV, cadex.Geom.Point theValue) |
| void | D1 (double theParameterU, double theParameterV, cadex.Geom.Point theValue, cadex.Geom.Vector theD1U, cadex.Geom.Vector theD1V) |
| void | D2 (double theParameterU, double theParameterV, cadex.Geom.Point theValue, cadex.Geom.Vector theD1U, cadex.Geom.Vector theD1V, cadex.Geom.Vector theD2U, cadex.Geom.Vector theD2V, cadex.Geom.Vector theD2UV) |
| bool | DN (double theParameterU, double theParameterV, uint theDerivativeOrder, cadex.Geom.Point theValue, cadex.Collections.VectorList theD) |
| Returns true if calculation was passed succsesfully, the returned vectors gives the value of the derivative for the order of derivation theDerivativeOrder. | |
| void | Curvature (double theParameterU, double theParameterV, cadex.Geom.Direction thePrincipalMaxDirection, cadex.Geom.Direction thePrincipalMinDirection) |
| void | Curvature (double theParameterU, double theParameterV, cadex.Geom.Direction thePrincipalMaxDirection, cadex.Geom.Direction thePrincipalMinDirection, out double theMaxCurvature, out double theMinCurvature) |
| void | Mirror (cadex.Geom.Point thePoint) |
| void | Mirror (cadex.Geom.Axis1d theAxis) |
| void | Mirror (cadex.Geom.Axis3d theAxis) |
| cadex.Geom.Surface | Mirrored (cadex.Geom.Point theRef) |
| cadex.Geom.Surface | Mirrored (cadex.Geom.Axis1d theAxis) |
| cadex.Geom.Surface | Mirrored (cadex.Geom.Axis3d theAxis) |
| void | Rotate (cadex.Geom.Axis1d theAxis, double theAngle) |
| cadex.Geom.Surface | Rotated (cadex.Geom.Axis1d theAxis, double theAngle) |
| void | Translate (cadex.Geom.Vector theVector) |
| cadex.Geom.Surface | Translated (cadex.Geom.Vector theVector) |
| void | Scale (cadex.Geom.Point thePoint, double theScale) |
| cadex.Geom.Surface | Scaled (cadex.Geom.Point thePoint, double theScale) |
 Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.Geometry Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.Geometry | |
| Geometry (global::System.IntPtr cPtr, bool cMemoryOwn) | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.BaseObject Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.BaseObject | |
| BaseObject (global::System.IntPtr cPtr, bool cMemoryOwn) | |
| void | Dispose () |
| bool | IsNull () |
| ulong | Id () |
| Return unique identifier of public object. | |
| bool | IsEqual (cadex.BaseObject theObj) |
| override int | GetHashCode () |
| override bool | Equals (System.Object o) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static new bool | CompareType (cadex.BaseObject theObject) |
| static new cadex.Geom.SurfaceOfRevolution | Cast (cadex.Geom.Surface theBase) |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.SweptSurface Static Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.SweptSurface | |
| static new bool | CompareType (cadex.BaseObject theObject) |
| static cadex.Geom.SweptSurface | Cast (cadex.Geom.Surface theBase) |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.Surface Static Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.Surface | |
| static new bool | CompareType (cadex.BaseObject theObject) |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.Geometry Static Public Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.Geometry | |
| static bool | CompareType (cadex.BaseObject theObject) |
| static cadex.Geom.Geometry | Cast (cadex.BaseObject theBase) |
Protected Member Functions | |
| override void | Dispose (bool disposing) |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.SweptSurface Protected Member Functions inherited from cadex.Geom.SweptSurface | |
| override void | Dispose (bool disposing) |
Defines a surface of revolution.
Surface of revolution is defined by a basis curve and a rotation axis. The following image depicts an example of a surface of revolution:
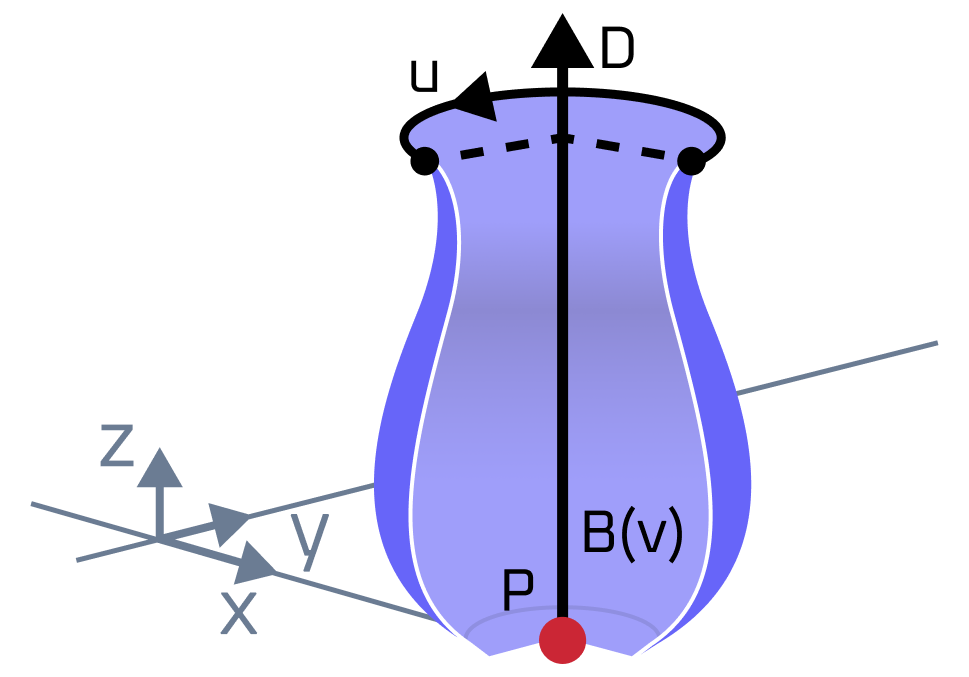
A surface of revolution is parametrized as follows: \(\mathbf{S}(u,v) = \mathbf{Z}(v) + \cos(u)(\mathbf{B}(v) - \mathbf{Z}(v)) + \mathbf{D}\times\sin(u)(\mathbf{B}(v) - \mathbf{Z}(v))\), where:
U-parameter is an angle of rotation around the axis counterclockwise, and V-parameter is s a parameter along the curve \(\mathbf{B}(v)\). Thus, U-isolines are correspond to curve \(\mathbf{B}(v)\) rotated around the rotation axis and V-isolines are circles perpendicular to rotation axis with radius equal to distance from the axis to a point on the basis curve at parameter V. U-isoline at \(u=0\) is the basis curve itself.
The curve \(\mathbf{B}(v)\) should be planar although this is not enforced. It should not cross the rotation axis, except possibly at the end points.
Surface or revolution is periodic along U with period \(2\pi\). It is V-periodic if the basis curve is periodic itself.
If a face lies on a full range of U its boundary wire will contain two seam-edges at parameters UMin() and UMax(). Likewise, if the surface is V-periodic the wire will contain two seam-edges at parameters VMin() and VMax(). If the basis curve has end point(s) lying on a rotation axis then the wire will contain degenerated edge(s) at respective point(s).
|
inline |
Constructor.
|
inlineprotectedvirtual |
Reimplemented from cadex.Geom.Surface.
|
inline |
Returns the value specified in the constructor.
Returns an origin point of a rotation axis.