Face Face.hxx cadex/ModelData/Face.hxx. More...
Public Member Functions | |
| __init__ (self, *args) | |
| ParametricDomain (self) | |
| Append (self, *args) | |
| Adds a wire to the face. | |
| Surface (self) | |
| Returns underlying surface. | |
| OuterWire (self) | |
| Returns outer wire. | |
| Triangulation (self) | |
| Returns triangulation of the face. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from manufacturingtoolkit.CadExMTK.ModelData_Shape Public Member Functions inherited from manufacturingtoolkit.CadExMTK.ModelData_Shape | |
| Type (self) | |
| Returns a shape type. | |
| Orientation (self) | |
| Returns orientation flag. | |
| Reversed (self) | |
| Returns a shape that shares the same geometry and subshape graph but has opposite orientation. | |
| Oriented (self, theOrientation) | |
| Returns a shape that shares the same geometry and subshape graph and has specified orientation. | |
| IsEqual (self, theOther) | |
| Returns true if the shape shares the same geometry and subshape graph, and has equal orientation. | |
| IsSame (self, theOther) | |
| Returns true if the shape shares the same geometry and subshape graph. | |
| SetName (self, theName) | |
| Sets the name. | |
| Name (self) | |
| Returns the name. | |
| AddAssociatedPMI (self, *args) | |
| AssociatedPMI (self) | |
| Returns the PMI elements. | |
| __hash__ (self) | |
| __eq__ (self, other) | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from manufacturingtoolkit.CadExMTK.BaseObject Public Member Functions inherited from manufacturingtoolkit.CadExMTK.BaseObject | |
| Id (self) | |
| Return unique identifier of public object. | |
| IsNull (self) | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| Cast (*args) | |
| Overload 1: Cast operator. | |
| CompareType (theObject) | |
| Check the type of object. | |
Face Face.hxx cadex/ModelData/Face.hxx.
Defines a topological face.
The following image depicts an example of a face:

Face resides on a geometrical surface (returned by Surface()) and is bounded by one or several wires. A face must always have at least one explicit outer wire even if it corresponds to a naturally bounded surface (e.g. torus or a sphere).
Orientation() defines whether face normal matches the normal of the underlying surface, or is opposite to it.
Face wires must always be closed, both in 3D and in 2D (i.e. parametric space of the underlying surface). Therefore a face lying on a periodical surface on its full period must have an explicit seam-edge (an edge corresponding to surface boundaries).
A face outer wire can be distinguished using the OuterWire() method.
Face wires must be oriented such that they define a closed portion of material. If to look in the direction opposite to a surface normal, p-curves of an outer wire (taking into account edge orientations) must be oriented counter-clockwise, and p-curve of inner wires (if present) - clockwise. This ensures that the face has a finite area.
The following image depicts an example of face with two wires and p-curves in parametric space of the face surface. P-curves of edges with forward orientation are displayed in green, p-curves of edges with reversed orientation are displayed in red:

Face with two wires | 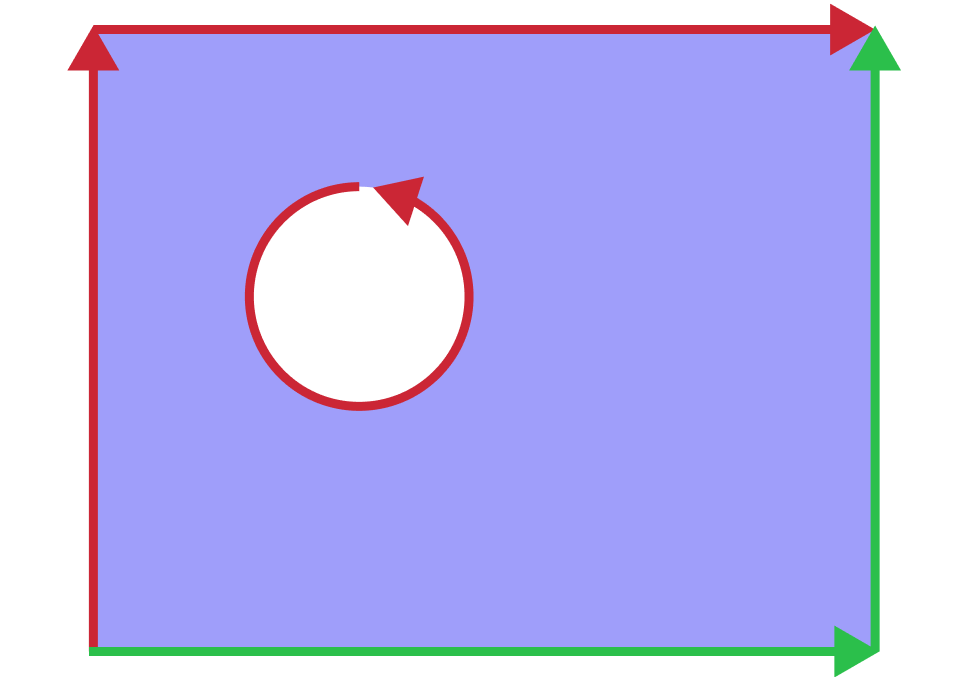
P-curves in surface parametric space |
The following code snippet demonstrates how to iterate over face edges p-curves:
Face p-curves define a closed contour (or a set of contours in the case of face with holes) in surface parametric space. A 2D bounding box in this surface parametric space can be returned using the Measurements.ComputeBoundingBox() method (its overload accepting ModelData.Face). The following images demonstrate a face lying on a cylindrical surface and its 2D contour and bounding box:
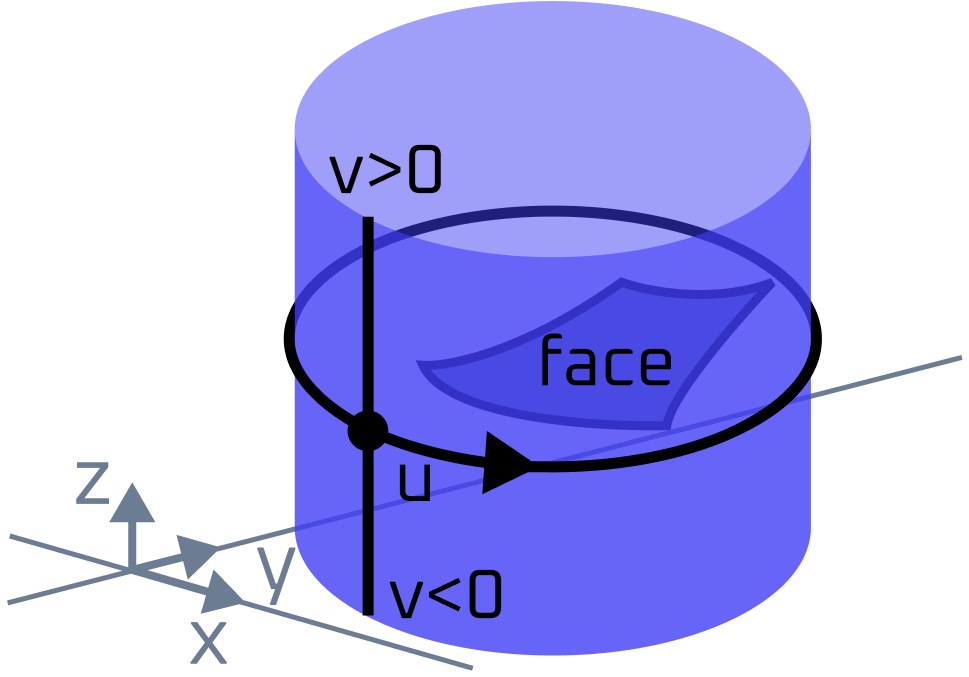
Face on cylindrical surface | 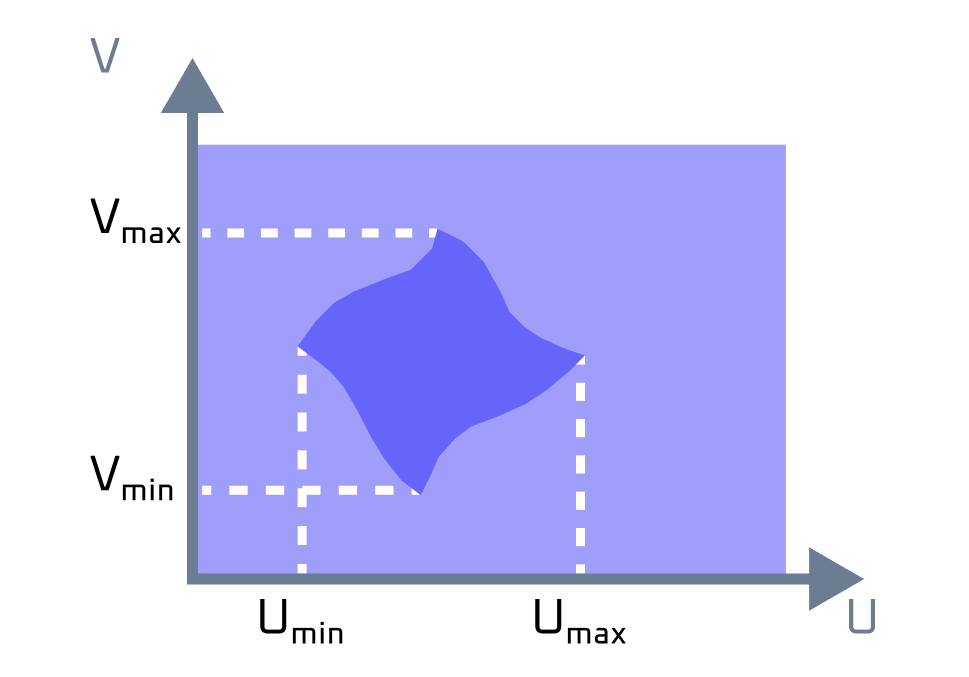
2D bounding box |
The following example demonstrates how to retrieve this bounding box. Note aHeight below would designate a 3D length of this cylindrical face and if it occupied entire U-range of the cylindrical surface (Geom.CylindricalSurface) then it would correspond to a cylinder's height:
| manufacturingtoolkit.CadExMTK.ModelData_Face.__init__ | ( | self, | |
| * | args ) |
Reimplemented from manufacturingtoolkit.CadExMTK.ModelData_Shape.
|
static |
Overload 1: Cast operator.
|
Overload 2: Cast operator.
Reimplemented from manufacturingtoolkit.CadExMTK.ModelData_Shape.
|
static |
Check the type of object.
Returns true if the specified object is this class type.
Reimplemented from manufacturingtoolkit.CadExMTK.ModelData_Shape.