Demonstrates how to perform unfolding of 3D model.
This example demonstrates how to perform unfolding of 3D model using sheet metal unfolder tool (SheetMetal_Unfolder). For this purpose, used a console application that imports a model, collects unique ModelData_Part s, traverses through unique ModelData_Part s, creates and runs SheetMetal_Unfolder, prints information about flat pattern parameters into console.
Unfolding will be performed for each unique ModelData_Part , but only for the scope of accepted geometries.
Application needs one input arguments to run:
For more information about unfolding visit Sheet Metal Unfolding page.
To explore the model and process ModelData_Part you need to derive a class from the ModelData_ModelElementVoidVisitor and override the part processing method void operator() (const ModelData::Part& thePart). In this example we use the PartProcessor class for this purpose. The operator() method is implemented to check each ModelData_Part for the presence of B-Rep Geometry and ModelData_Solid or ModelData_Shell shapes in it.
ProcessSolid and ProcessShell methods are used to run sheet metal unfolder for given entities.
To traverse only unique parts of the imported model, the ModelData_ModelElementUniqueVisitor class is used.
Method PrintFlatPattern is used to explore and print flat pattern parameters.
Below is the example output for model from ./examples/models/Part2.stp.
Model: Part2
Part #0 ["Part2"] - solid #0 has:
Flat Pattern with:
length: 220.712 mm
width: 167.838 mm
thickness: 1 mm
perimeter: 1121.37 mm
| ||
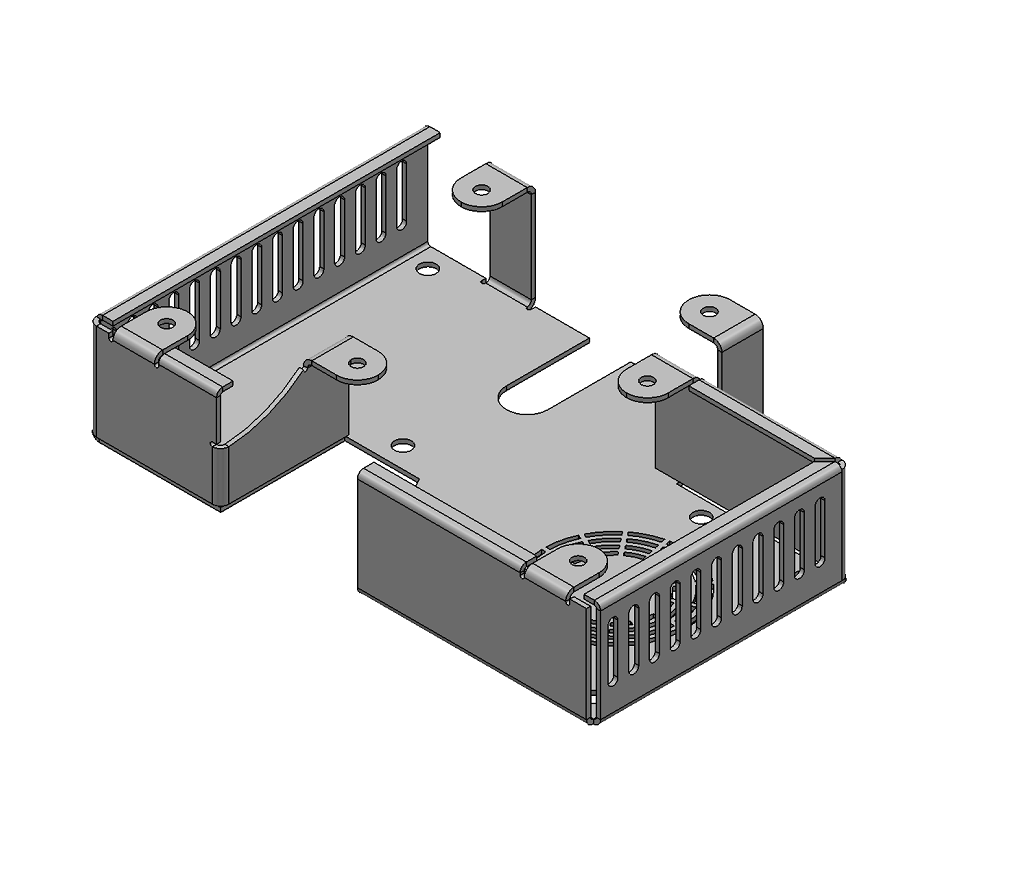
Original model | 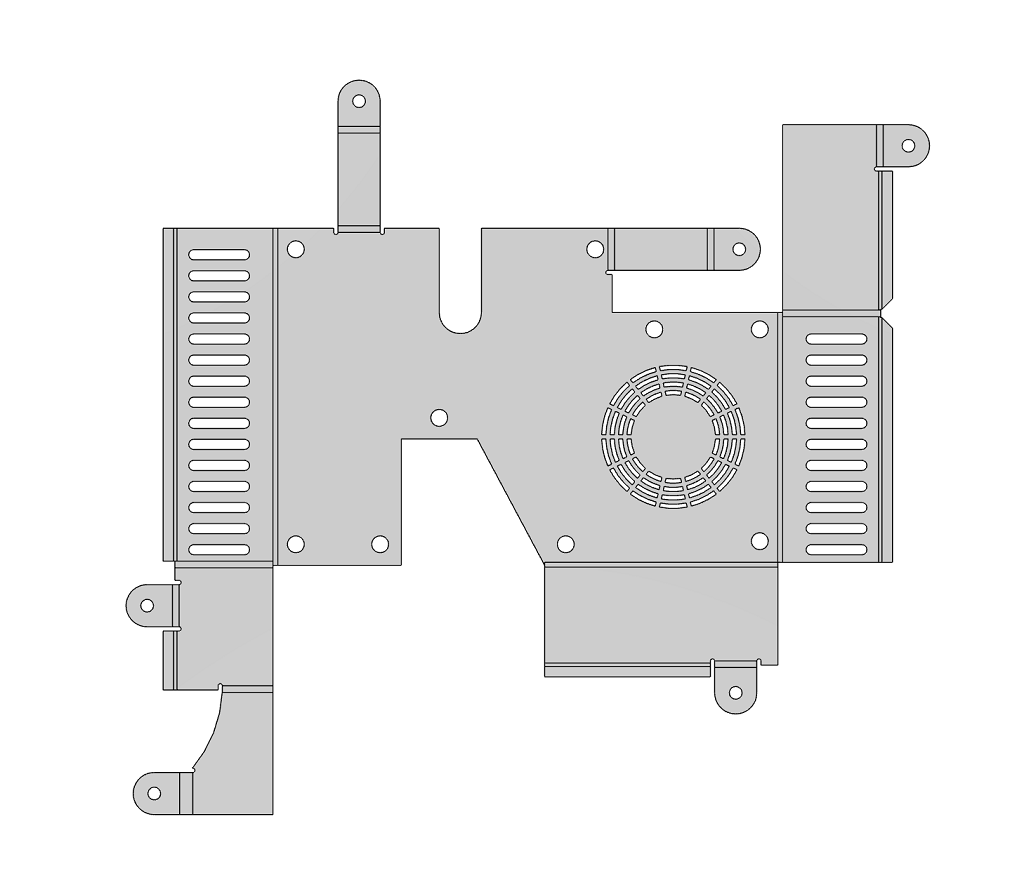
Unfolded view | |