| Issue | Description | Example |
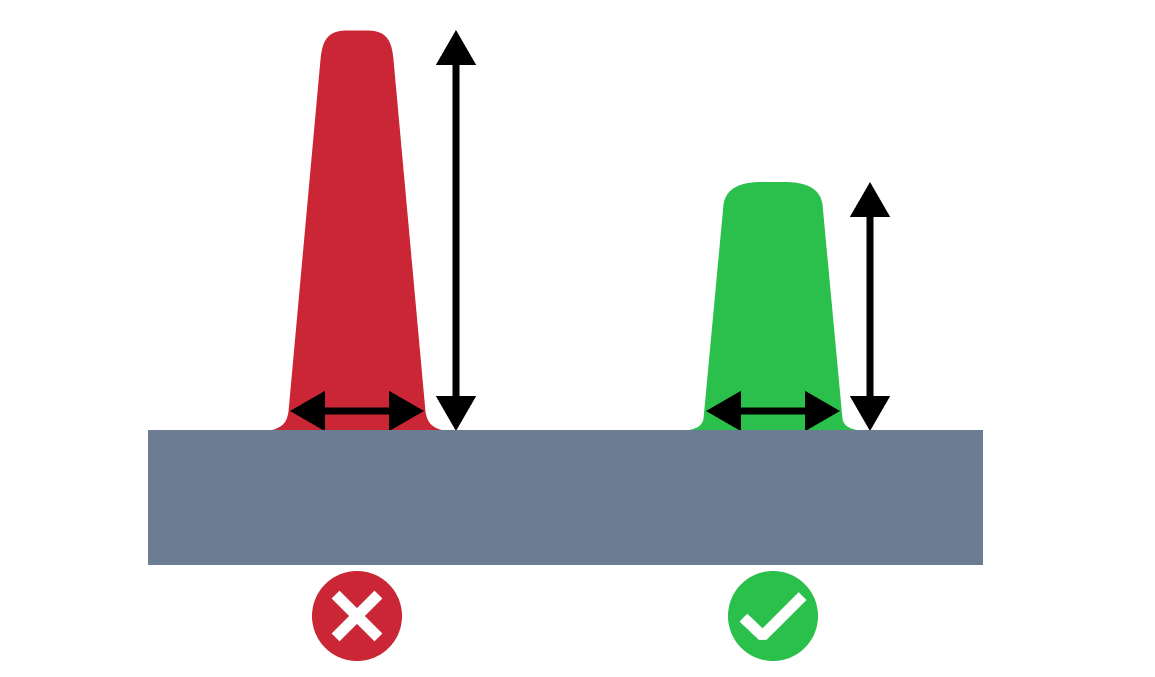
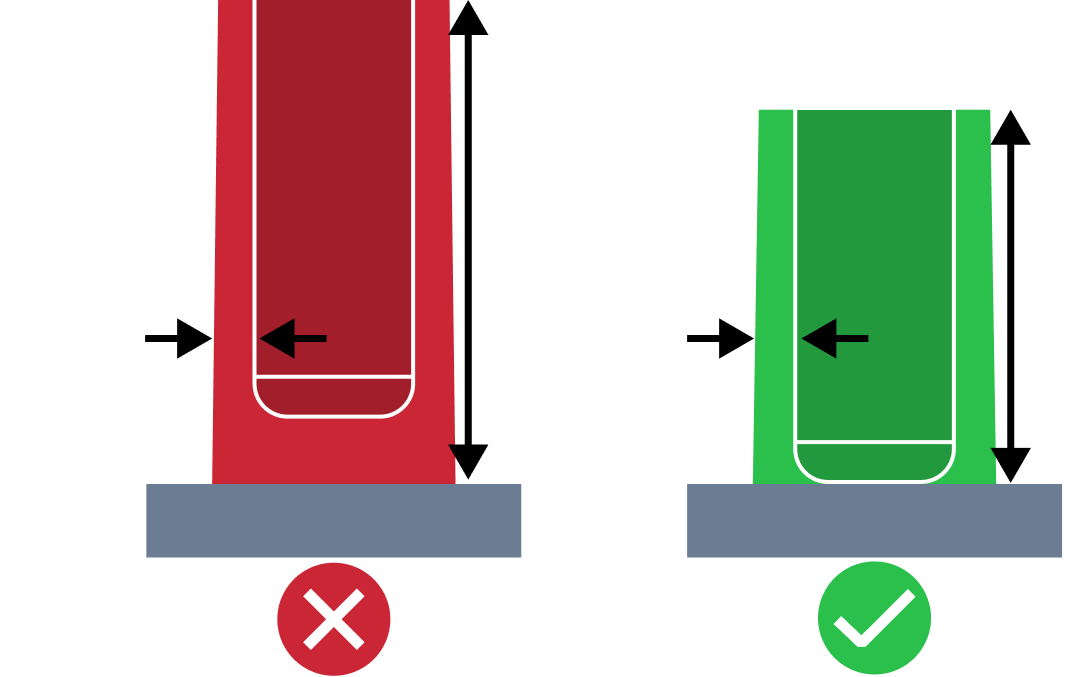
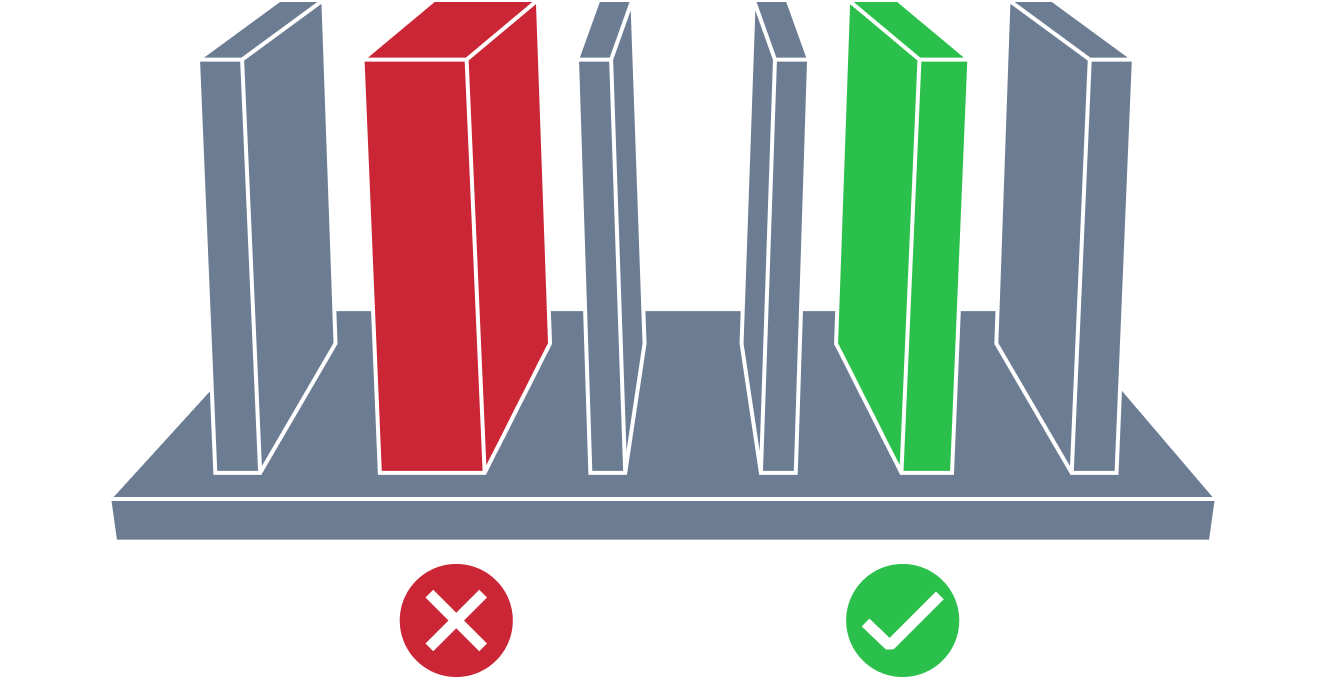
| High Rib | The high rib issue refers to a situation where the height of the rib is too high compared to the thickness of the rib. An appropriate height is required to facilitate removal of the part from the mold. |
|
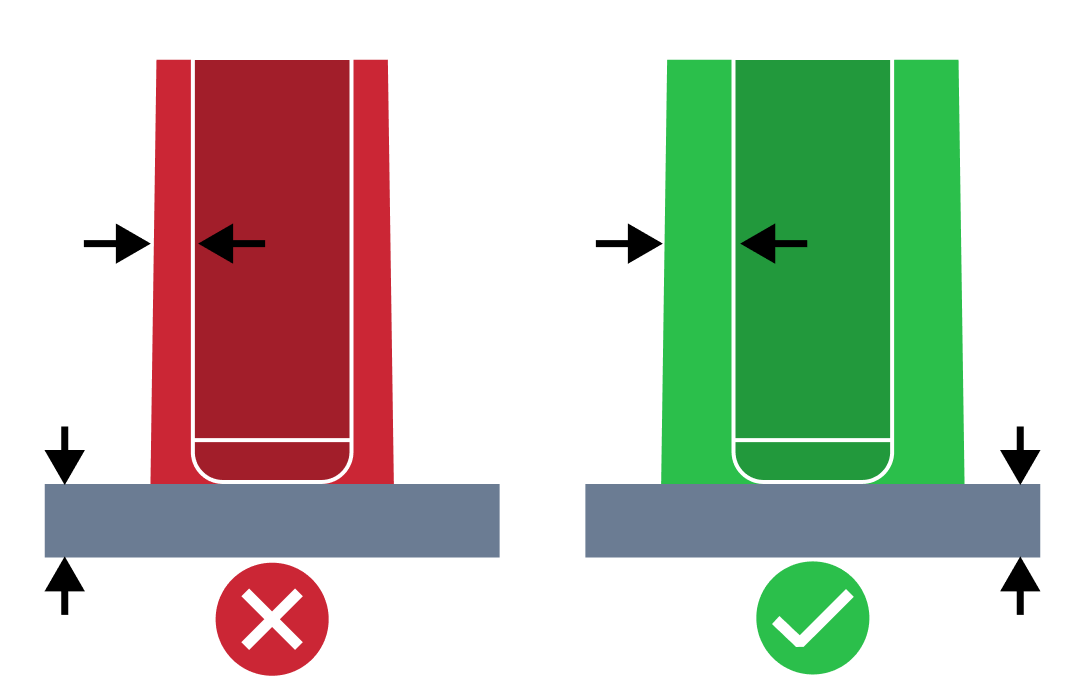
| Irregular Rib Thickness | The irregular thickness rib issues refers to a situation where the rib thickness is too big or small compared to the wall thickness. Proper thickness value is required to mitigate potential sinking issues and provide uniform cooling and shrinking. |
|
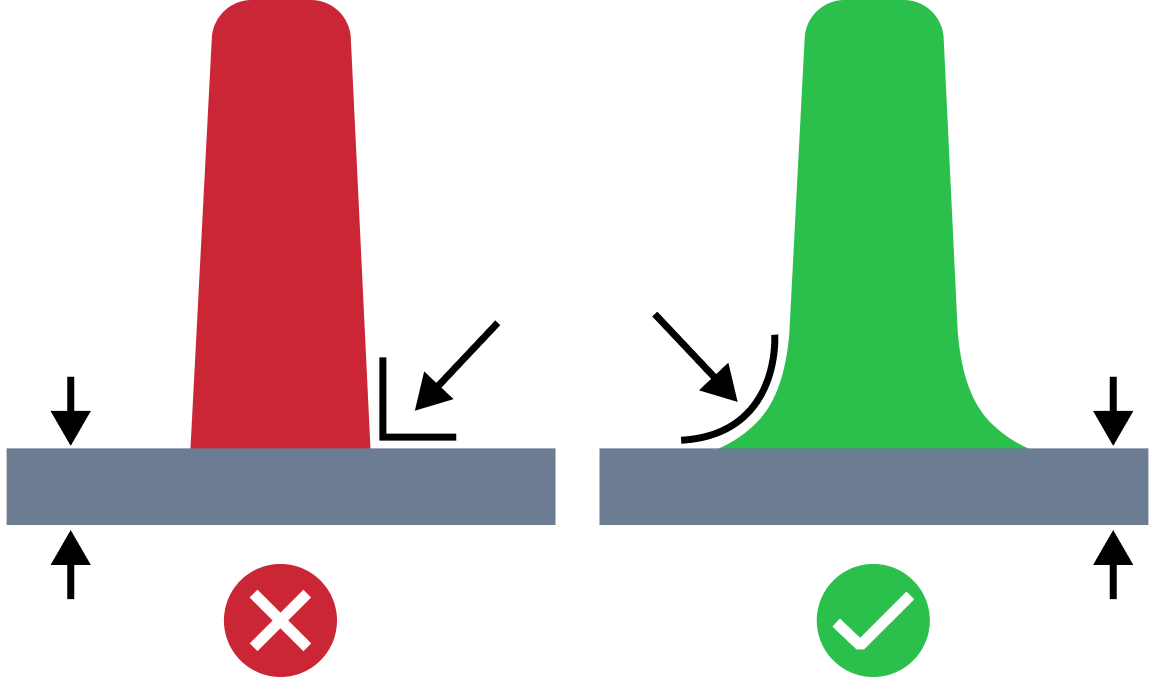
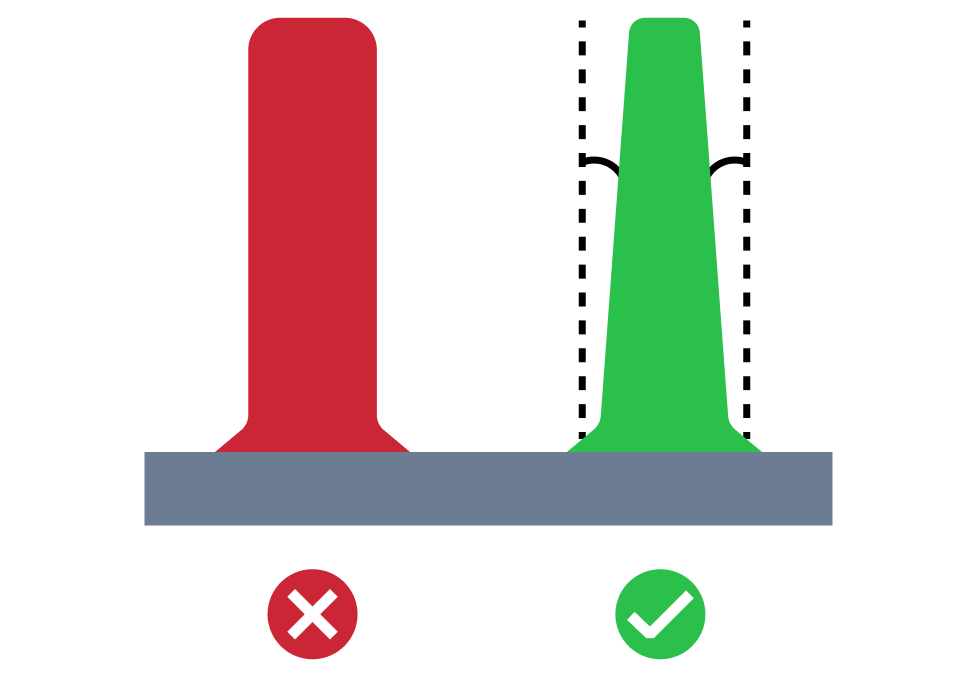
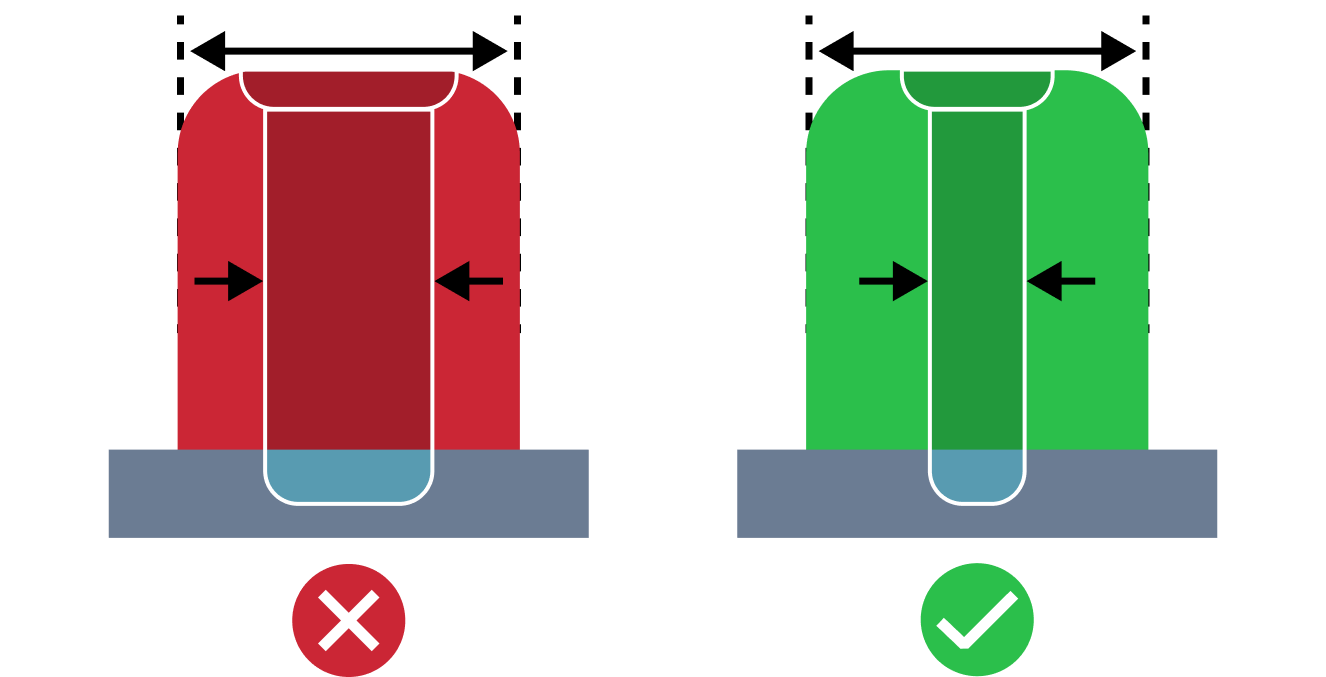
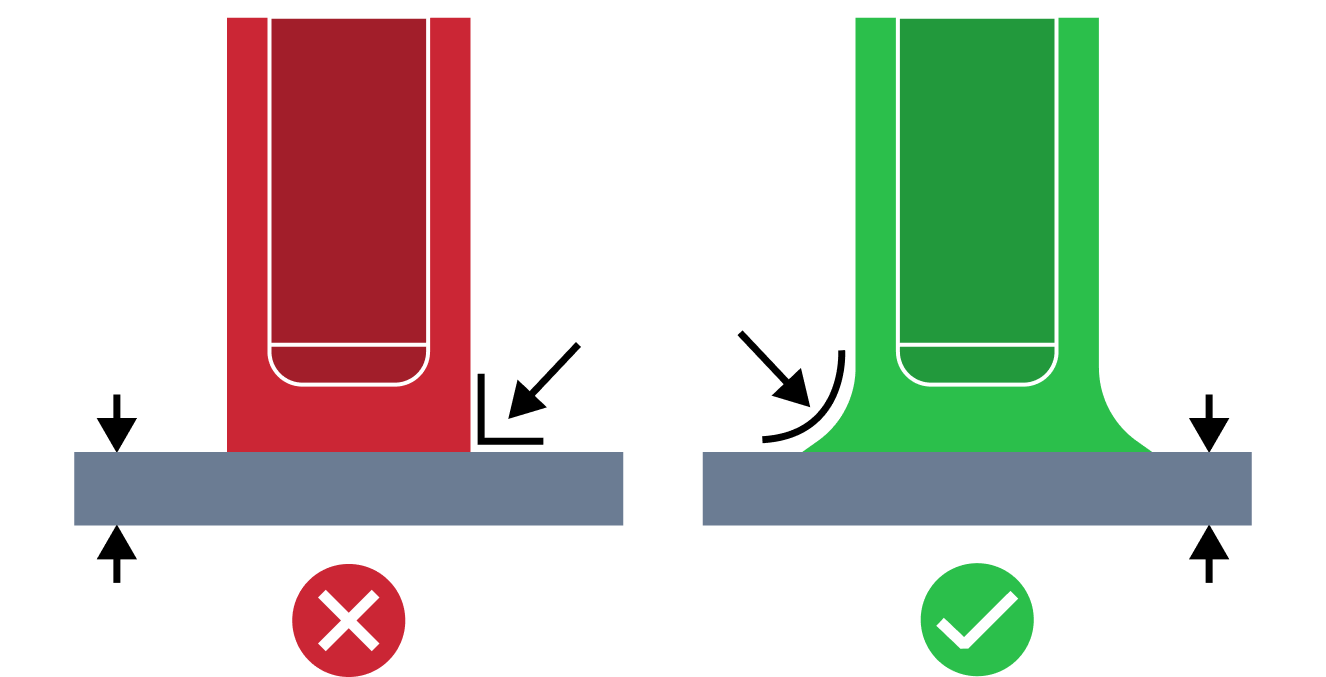
| Small Rib Base Radius | The small rib base radius issue refers to a situation where the base radius is too small compared to the wall thickness. Proper base radius value is required to minimize stress concentrations and mold ejection problems. |
|
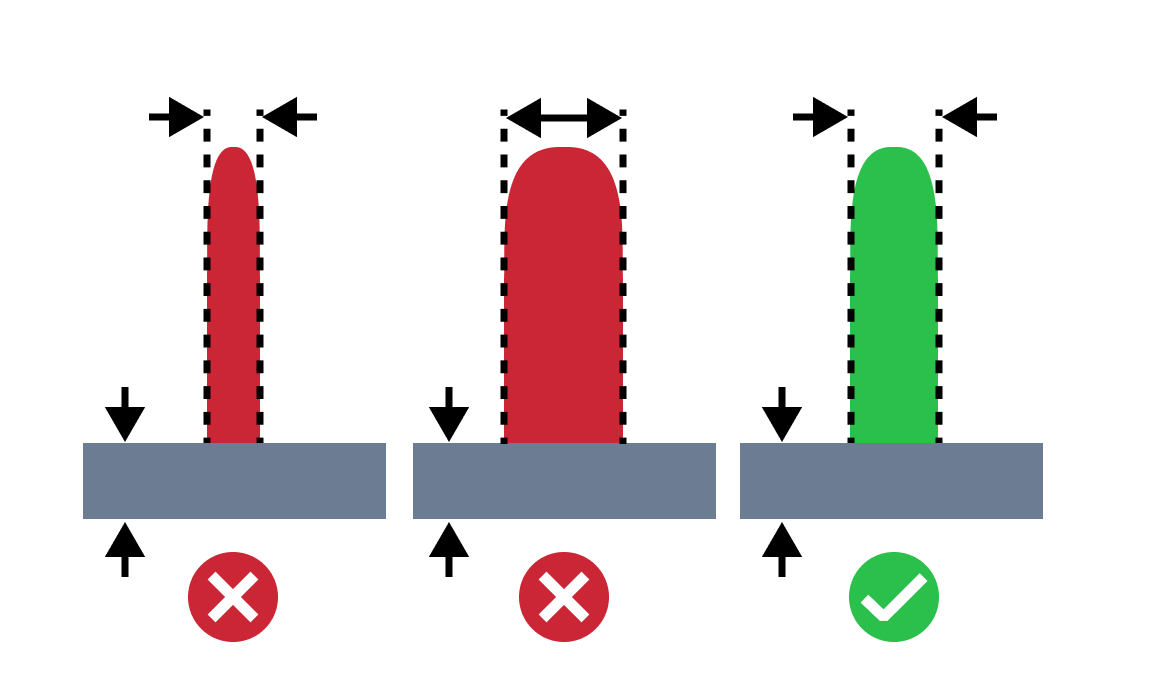
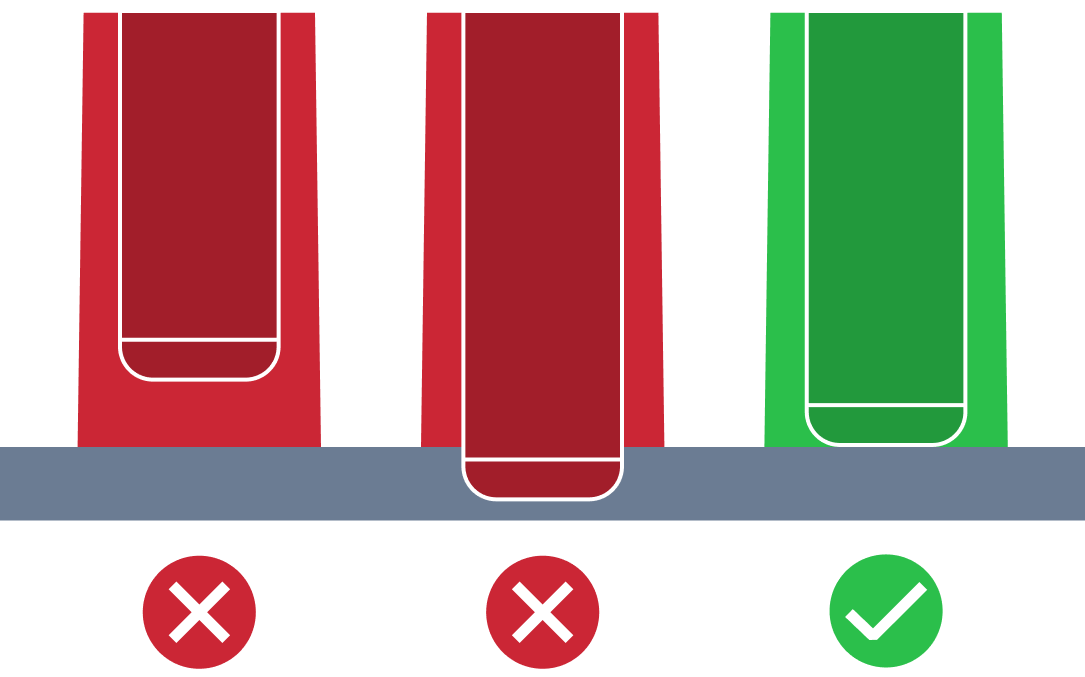
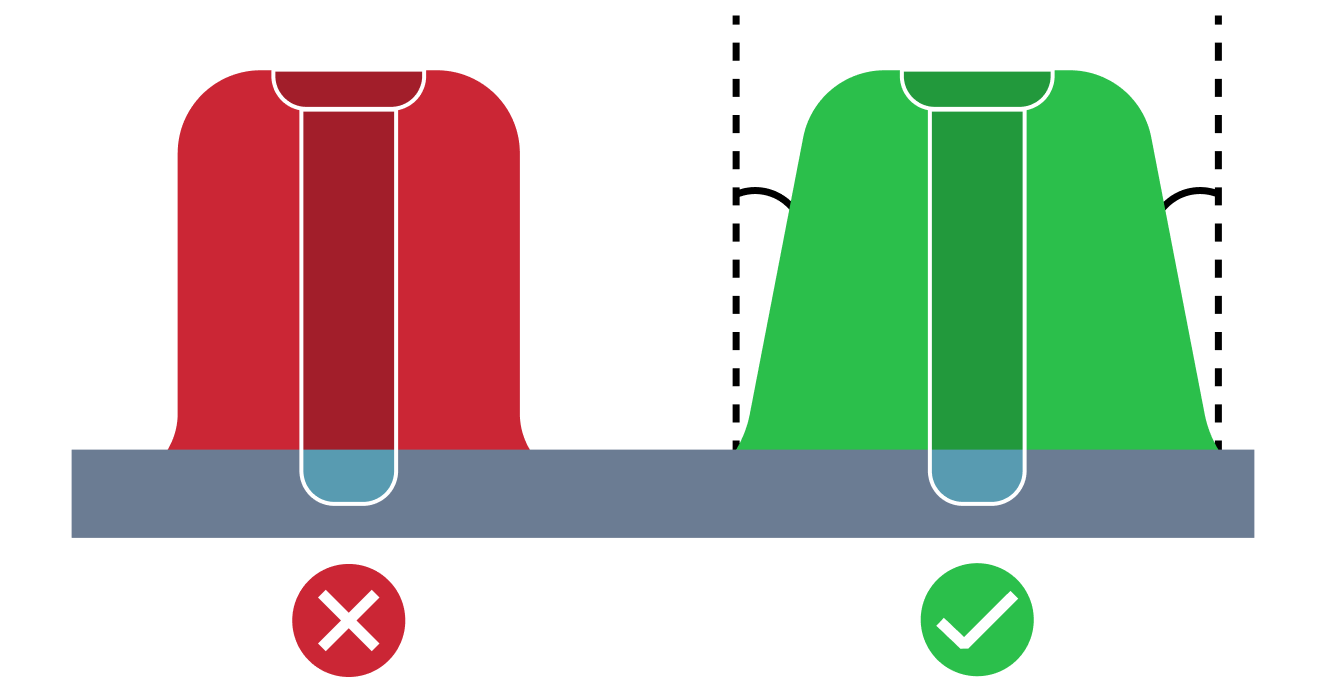
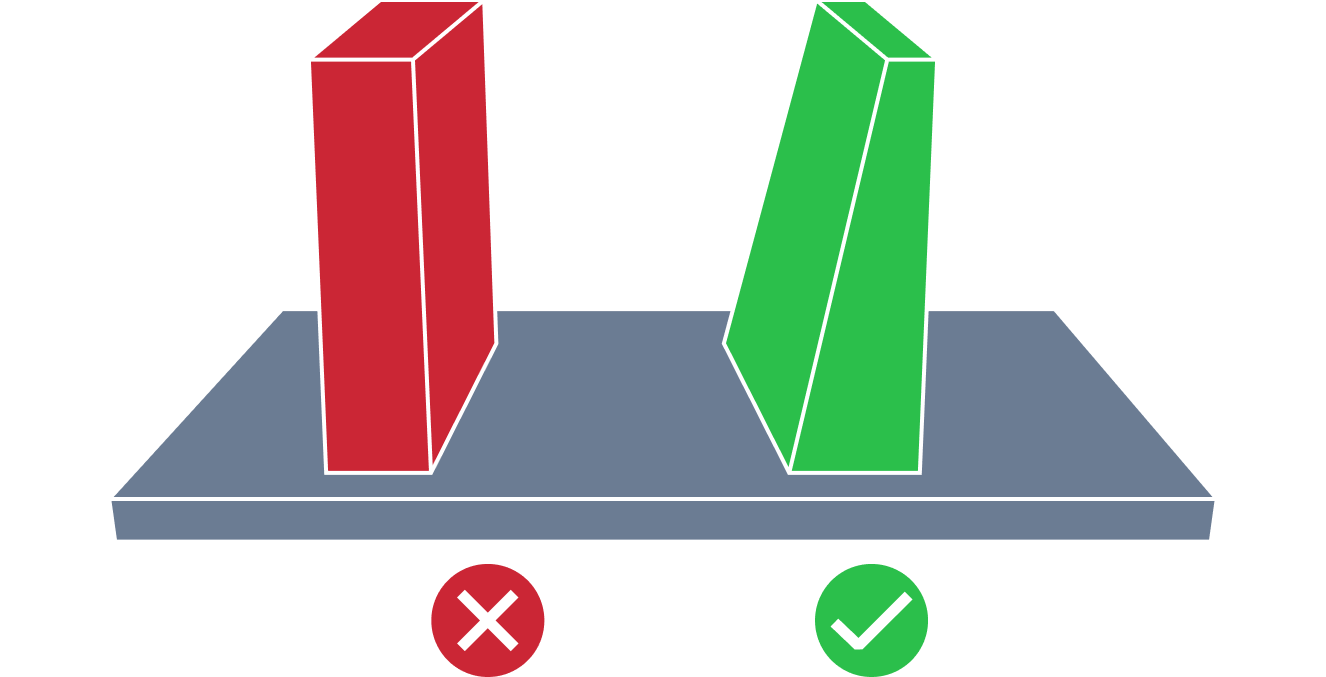
| Small Rib Draft Angle | The small rib draft angle issue refers to a situation where the rib draft angle is smaller than the recommended one. An appropriate draft angle is required to facilitate removal of the part from the mold and minimizing its damage. Also too small draft angle can lead to defects like drag marks. |
|
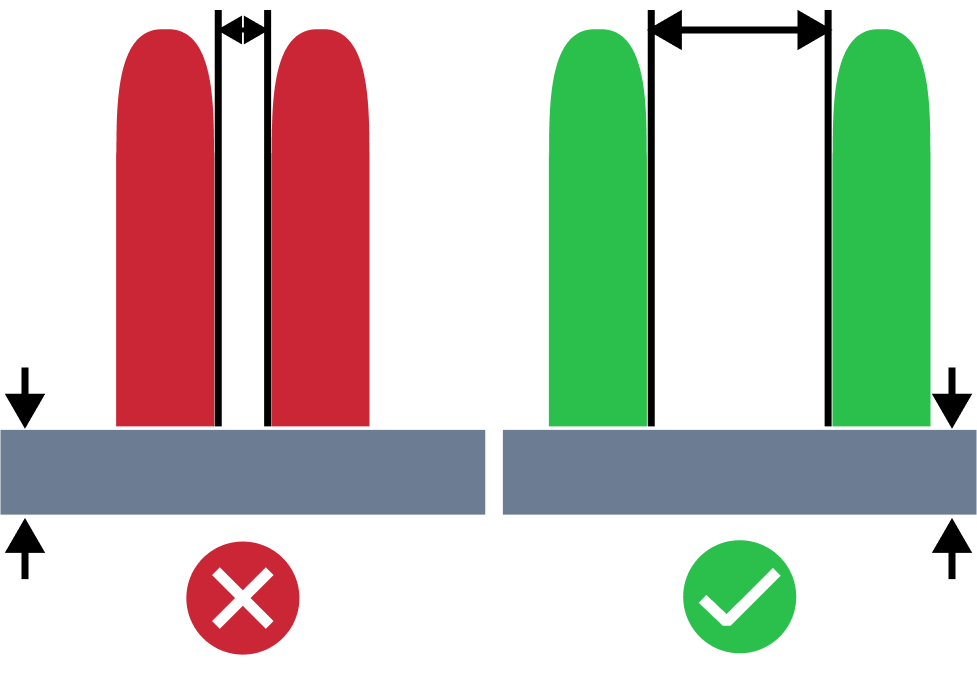
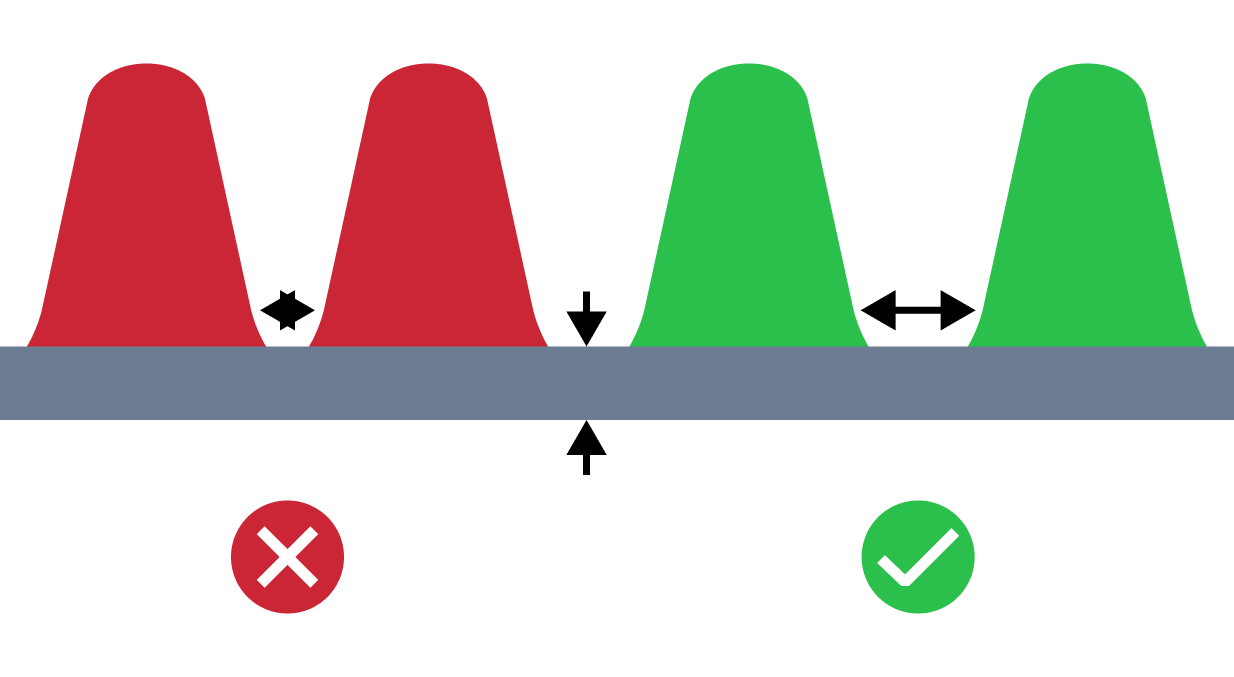
| Small Distance Between Ribs | The small distance between ribs issue refers to a situation where the distance between ribs is smaller than the recommended one. Proper distance between ribs are important to promotes even cooling and enhances structural integrity of the part. |
|
| High Screw Boss | The high screw boss issues refer to situation when the height of the boss is much greater compared to the thickness. High bosses are more susceptible to warping and shrinkage, and can also cause non-uniform cooling and blocking removal from the mold. Proper height value is required to avoid potential stress failures caused by thick regions. |
|
| Irregular Screw Boss Core Depth | The irregular core depth screw boss issues refer to situation when the height of the boss is not equal to core depth. Shallow holes can leave thick sections in the wall, while deeper holes reduce the surrounding wall thickness. To prevent aesthetic defects caused by inconsistent wall thicknesses, the core depth must be equal to the boss height. |
|
| Irregular Screw Boss Core Diameter | The irregular screw boss core hole diameter issue refers to a situation where the screw boss core hole diameter is too big or small compared to the outer diameter. Proper diameter value is required to mitigate potential stress failures or flow issues caused by thick regions. |
|
| Irregular Screw Boss Wall Thickness | The irregular wall thickness screw boss issues refers to the challenge of molding features with deviating from the nominal wall thickness. Irregular wall thickness screw boss can cause non-uniform cooling and fails applied loads. Therefore, it is recommended to maintain screw boss's thickness variance from 40% to 60% across the nominal thickness to minimize the risk of sinking or fracture. |
|
| Small Screw Boss Draft Angle | The small screw boss draft angle issue is similar to the rib small draft angle issue. Appropriate draft angles are crucial for smooth part ejection in molding. This is essential to prevent production challenges and optimize product quality. |
|
| Small Screw Boss Base Radius | The small screw boss base radius issue refers to a situation where the base radius is too small compared to the wall thickness. Proper base radius value is required to mitigate potential stress failures. |
|
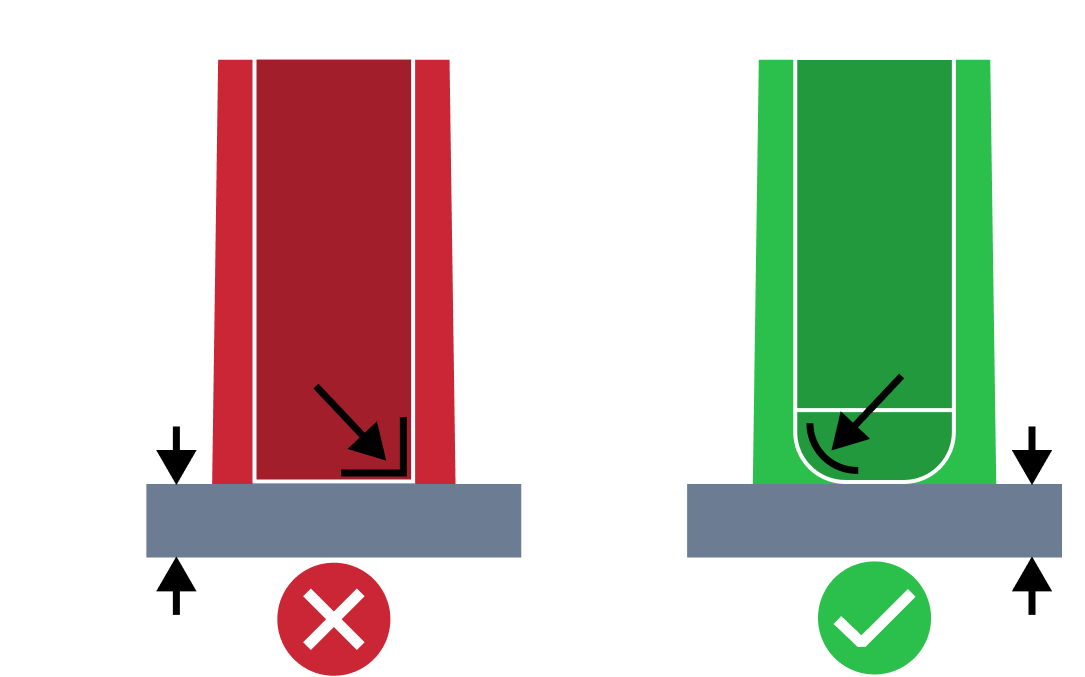
| Small Screw Boss Hole Base Radius | The small screw boss hole base radius issue refers to a situation where there is sharp corners at the base of the hole in a boss. Proper base radius value is required to minimize potential defects caused by failure of the core pin. |
|
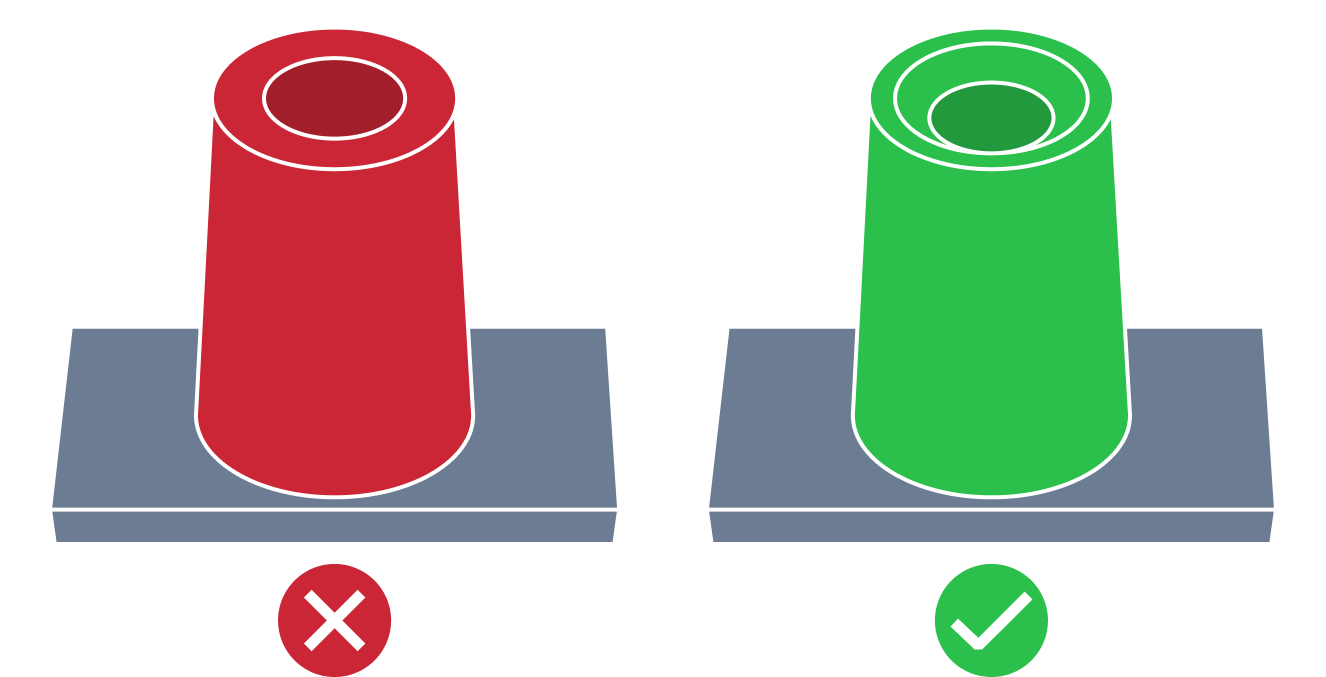
| Screw Boss Without Top Chamfer | The non chamfered screw boss issues refer to situation when the screw boss doesn't contain top chamfer. Screw boss top chamfer improves the lead-in for fasteners and facilitate assembly operations. Top chamfer is required to to reduce potential assembly difficulties. |
|
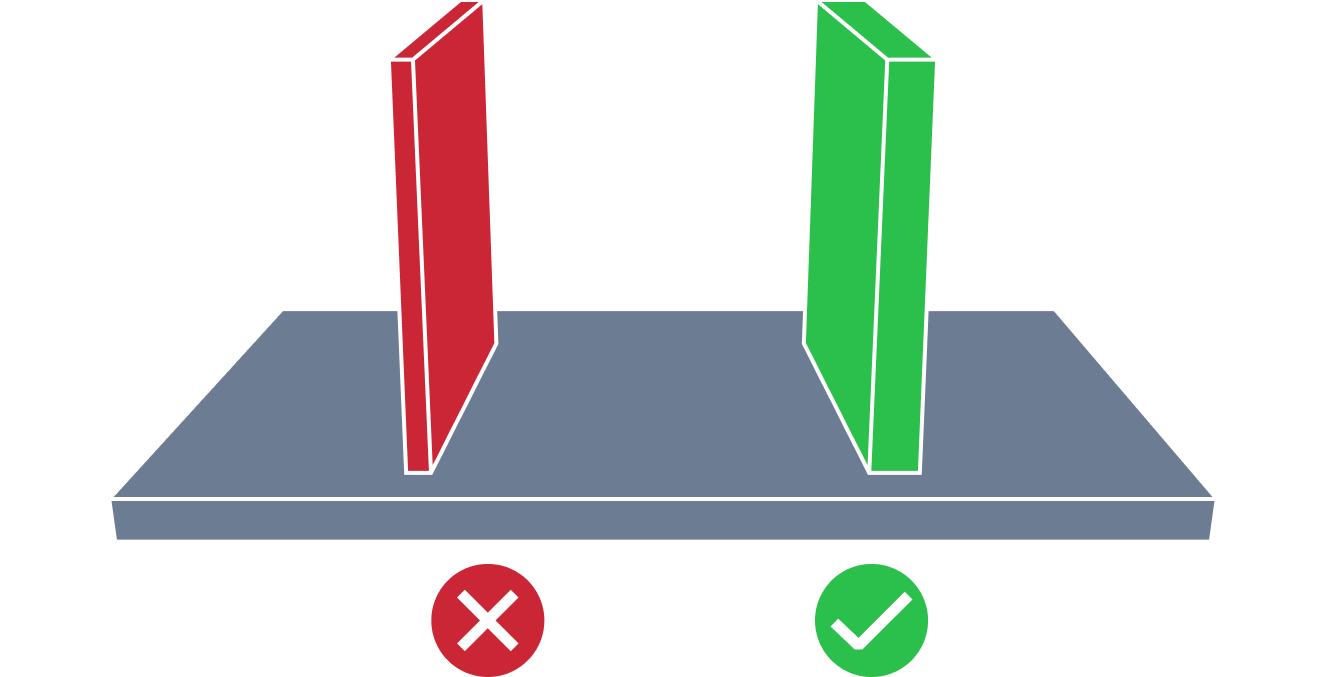
| Irregular Wall Thickness | Irregular wall thickness issue in molding design analysis refers to the challenge of molding features with wall thickness deviating from the average value. This can lead to uneven cooling and problems with shrinking during the molding process. Therefore, it is recommended to maintain wall thicknesses variance of 20% or less across the design’s wall thicknesses to limit potential structural and aesthetic issues. |
|
| Large Wall Thickness | Large wall thickness issue in molding design analysis refers to the challenge of molding features with overly thick walls. This can lead to difficulties such as uneven cooling, excessive material usage, and potential defects like voids or surface blemishes. The root causes typically involve inadequate cooling time, excessive injection pressure, or suboptimal material selection. Therefore, it is recommended to maintain wall thicknesses of 4.0 mm or less to prevent potential material flow problems and prolonged cooling times. |
|
| Small Wall Thickness | Small wall thickness issue in molding design analysis refers to the challenge of molding features with thin walls. This can result in challenges like warping, sink marks, and diminished strength. The root causes often include improper material flow, insufficient packing pressure, or flawed mold design. Therefore, it is recommended to maintain wall thicknesses at least 1.0 mm to avoid structurally weak or distorted parts. |
|
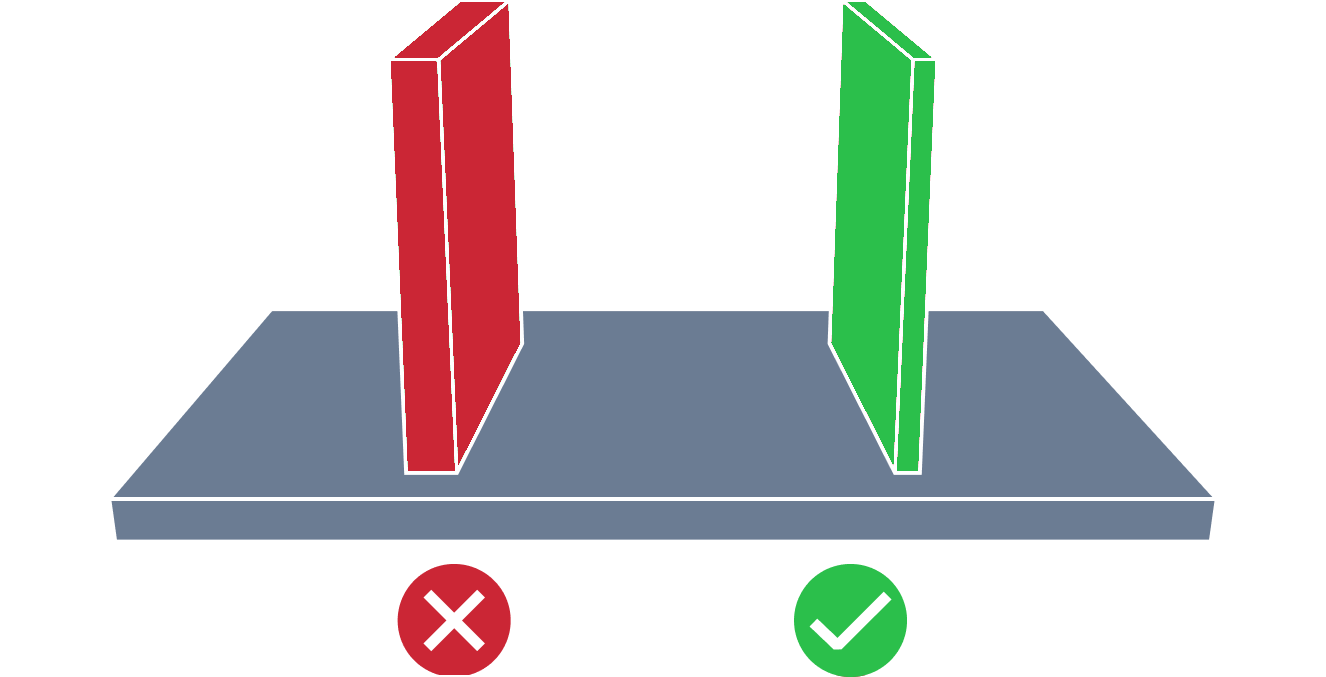
| Small Wall Draft Angle | The small wall draft angle issue refers to a situation where the wall draft angle is smaller than the recommended one. An appropriate draft angle is required to facilitate removal of the part from the mold and minimizing its damage. Also too small draft angle can lead to defects like drag marks. |
|
| Small Distance Between Bosses | Small distance between bosses issue in molding design analysis refers to the challenge of molding features with bosses placed very close to each other. This can result in challenges like warping, sink marks, and diminished strength. The root causes often include inadequate cooling due to thin areas between bosses, which can affect part quality. Therefore, it is recommended to maintain spacing between bosses at least twice the nominal thickness. |
|